If you are considering an esteemed CPA license or a specific certification in auditing, financial services, or fraud detection, these qualifications can open doors to impressive career prospects.
Pursuing further education not only shows your determination but also underlines your pursuit of professional growth—a trait greatly appreciated by current and prospective employers. It is important to understand which licenses or certifications are necessary in your line of work, industry, seniority, and more, as not every qualification listed below is required.
Accounting Certifications and Licenses
The accounting and finance field is vast and multifaceted, encompassing a variety of specialties and roles that require specific skills and knowledge. To establish expertise and enhance career prospects, professionals often pursue certifications that validate their proficiency in particular areas.
Among the most prominent licenses and certifications are the Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Certified Management Accountant (CMA), Certified Internal Auditor (CIA), and Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE), each catering to distinct segments of the industry.
These achievements signal a high level of competence to employers and offer pathways to advanced career opportunities and specialized roles. In addition to these, several other certifications address various niche aspects of accounting and finance, providing professionals with the flexibility to tailor their credentials to their career goals.
Certified Public Accountant (CPA)
The Certified Public Accountant (CPA) license is widely regarded as one of the most prestigious and significant credentials in the accounting and finance industry. It is a benchmark of expertise, competence, and ethical standards, crucial in ensuring financial transparency and regulatory compliance within organizations.
Significance of a CPA License
- Expertise and Competence: The CPA license signifies a high level of knowledge and proficiency in accounting principles, financial reporting, auditing, and tax regulations. CPAs are trusted advisors who provide critical insights for decision-making, financial planning, and strategic growth.
- Financial Transparency: CPAs play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of financial reporting. They conduct thorough audits and ensure that financial statements are accurate and comply with applicable laws and standards, fostering trust among stakeholders, investors, and regulatory bodies.
- Regulatory Compliance: The CPA designation is integral to navigating the complex landscape of financial regulations. CPAs are well-versed in the latest laws and guidelines, ensuring that businesses adhere to regulatory requirements, thus avoiding legal penalties and enhancing their reputation.
Rigorous Requirements for Obtaining a CPA License
The path to becoming a CPA is challenging, reflecting the high standards expected of professionals in this field. The requirements typically include:
- Education: Candidates must complete at least 150 semester hours of college coursework, often more than a standard bachelor’s degree. This education must cover specific accounting and business-related subjects, ensuring solid foundational knowledge.
- Uniform CPA Exam: Aspiring CPAs must pass the Uniform CPA Examination, a rigorous test comprising four sections: Auditing and Attestation (AUD), Business Environment and Concepts (BEC), Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR), and Regulation (REG). The exam is designed to assess the candidate’s technical skills and understanding of core concepts in accounting and finance.
- Work Experience: Most states require candidates to have a certain amount of relevant work experience, typically one to two years, under the supervision of a licensed CPA. This practical experience ensures that candidates are exposed to the profession’s demands and challenges in the real world.
- Ethics Exam: Many states also mandate completing an ethics exam, emphasizing the importance of ethical conduct and professional integrity in accounting practices.
Importance in Ensuring Financial Transparency and Regulatory Compliance
CPAs are at the forefront of safeguarding the financial health of organizations and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. Their expertise helps in:
- Conducting Audits: CPAs perform independent audits that assure the accuracy of financial statements, which is crucial for investor confidence and market stability.
- Tax Compliance: They assist businesses and individuals in navigating complex tax regulations, ensure compliance, and optimize tax liabilities.
- Financial Advisory: CPAs offer strategic financial advice, helping organizations plan for future growth, manage risks, and make informed financial decisions.
3 Key Reasons to Consider Pursuing a CPA:
- Retirement Gap and Imminent Demand: According to the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), 75% of current CPAs are expected to retire within the next five years. This significant turnover will create a substantial demand for new CPAs to fill these roles.
- Upper-Level Management: Many upper-level management positions, especially in tax and audit services, require a CPA license. Holding a CPA opens doors to senior roles and leadership positions within organizations.
- Educational Shortfall: Colleges are struggling to fill accounting courses, leading to a shortage of qualified graduates entering the profession. This scarcity underscores the value of obtaining a CPA to stand out in the job market and capitalize on the high demand.
Distinction from Other Certifications
While other certifications in accounting and finance, such as the CMA, CIA, and CFE, can differentiate applicants, the CPA is uniquely essential. It is not just a distinguishing factor but a foundational requirement for many high-level roles and notable accounting companies. Other certifications help enhance specific skills or knowledge areas, but the CPA remains the gold standard, providing comprehensive expertise and credibility.
In summary, the CPA license symbolizes a commitment to excellence, ethical practice, and continuous learning. It not only enhances career prospects but also upholds the standards necessary for a transparent and compliant financial ecosystem. The impending retirement wave, coupled with the shortage of new graduates, makes pursuing a CPA more crucial than ever, ensuring that you are well-positioned to meet the industry’s evolving demands.
Certified Internal Auditor (CIA)
The Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) certification is a globally recognized credential that signifies expertise in internal auditing, internal controls, and risk management. It plays a critical role in enhancing an organization’s governance, risk management, and control processes, thereby maintaining transparency and integrity in financial management.
Significance of CIA Certification
- Expertise in Internal Controls: The CIA certification validates a professional’s ability to design, assess, and improve internal controls. This is crucial for ensuring that an organization’s operations are efficient, compliant with regulations, and free from significant risks.
- Risk Management Proficiency: CIAs are equipped with the skills to identify and assess financial and operational risks. They provide valuable insights on how to mitigate these risks, which is essential for protecting the organization’s assets and reputation.
- Operational Efficiency: By evaluating internal processes and recommending improvements, CIAs help organizations enhance their operational efficiency. This contributes to more effective management practices and better allocation of resources.
CIA Certification Requirements
To obtain the CIA certification, candidates must meet rigorous requirements that ensure they are well-prepared to handle the complexities of internal auditing.
CIA Exam: Candidates must pass the CIA exam, which consists of three parts:
- Essentials of Internal Auditing
- Practice of Internal Auditing
- Business Knowledge for Internal Auditing
This comprehensive exam tests candidates’ understanding of internal auditing standards, practices, and principles.
Ethics and Continuing Education: CIAs must adhere to a strict code of ethics and engage in continuing education to keep their knowledge and skills current.
Importance in 5 Highly Regulated Industries
The CIA certification is particularly valuable in industries that are subject to stringent regulations and require robust internal controls to ensure compliance and manage risks effectively. These industries include:
- Big Four Accounting Firms: These firms demand the highest standards of internal audit practices to ensure the accuracy and reliability of their audits and consulting services.
- Banking: CIAs help banks manage financial risks, comply with regulatory requirements, and maintain the integrity of their financial reporting systems.
- Insurance: In the insurance sector, CIAs assess risks related to underwriting, claims, and financial operations, ensuring that companies adhere to industry regulations and standards.
- Healthcare: With its complex regulatory environment, the healthcare industry relies on CIAs to evaluate internal controls and ensure compliance with health laws and regulations.
- Financial Services: Financial service firms benefit from CIAs who can identify and mitigate risks, ensuring that financial transactions and operations are conducted transparently and securely.
Enhancing Organizational Integrity
CIAs contribute to maintaining transparency and integrity within organizations. Their role includes:
- Assessing Financial Risks: CIAs identify potential financial threats and vulnerabilities, providing management with actionable insights to mitigate these risks.
- Evaluating Internal Processes: By examining the effectiveness and efficiency of internal processes, CIAs help organizations streamline operations and enhance performance.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency: Recommendations made by CIAs lead to improvements in operational processes, reducing waste and improving resource allocation.
The CIA certification is integral to ensuring robust internal controls and effective risk management within organizations. It equips professionals with the expertise needed to assess financial risks, evaluate internal processes, and enhance operational efficiency, which is vital for maintaining transparency and integrity in financial management.
Highly regulated industries such as accounting, banking, insurance, healthcare, and financial services particularly benefit from the specialized knowledge and skills that CIAs bring to their roles.
Certified Management Accountant (CMA)
The Certified Management Accountant (CMA) certification is a prestigious credential that plays a strategic role in financial planning, analysis, and decision-making within organizations. It equips professionals with advanced management accounting skills, empowering them to drive business performance, optimize financial strategies, and navigate complex financial transactions effectively.
Strategic Role of CMA Certification
- Advanced Management Accounting Skills: The CMA certification provides in-depth knowledge of management accounting principles, including budgeting, forecasting, cost management, and performance evaluation. This expertise is crucial for professionals tasked with steering an organization’s financial health and strategic direction.
- Financial Planning and Analysis: CMAs are adept at financial planning and analysis (FP&A), a critical function that involves preparing detailed financial forecasts, conducting variance analysis, and interpreting financial data to support strategic decision-making. This enables organizations to anticipate market trends, allocate resources efficiently, and achieve long-term financial goals.
- Decision-Making: The CMA certification emphasizes strategic decision-making skills, teaching professionals how to analyze financial information, assess risks, and make informed decisions that drive business performance. CMAs provide actionable insights that help organizations capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
Empowering Business Performance
- Driving Business Performance: CMAs play a vital role in enhancing business performance by implementing robust financial strategies and operational improvements. They utilize advanced analytics to identify key performance indicators (KPIs) and monitor progress towards strategic objectives.
- Optimizing Financial Strategies: CMAs are experts in optimizing financial strategies, ensuring that an organization’s financial practices align with its overall business goals. They focus on areas such as cost control, investment appraisal, and capital budgeting to maximize profitability and efficiency.
- Navigating Complex Financial Transactions: CMAs possess the skills needed to navigate complex financial transactions, such as mergers and acquisitions, financial restructuring, and corporate financing. Their expertise ensures that these transactions are conducted smoothly and align with the organization’s strategic interests.
Financial Benefits and Industry Demand
According to a report by the Miami Herald, CMAs make approximately 21% more than non-certified accounting professionals. This significant salary advantage reflects the high demand for CMAs and the value they bring to their organizations.
The CMA certification is sought after across a wide range of industries. Industries include:
- Finance: CMAs help financial institutions manage costs, improve financial reporting, and develop strategic plans.
- Insurance: In the insurance sector, CMAs optimize risk management strategies and enhance financial performance.
- Real Estate: CMAs in real estate analyze market trends and manage financial portfolios to drive profitability.
- Education: Educational institutions benefit from CMAs who manage budgets and financial planning.
- Wholesale and Retail Trade: CMAs improve inventory management, cost control, and financial planning in wholesale and retail businesses.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, CMAs streamline production costs and improve financial efficiency.
- Communication: CMAs in communication firms enhance financial reporting and strategic planning.
- Transportation: Transportation companies rely on CMAs to optimize operational costs and improve financial performance.
- Construction: CMAs help construction firms manage project costs and financial risks effectively.
Enhancing Organizational Success Through a CMA
The CMA certification plays a strategic role in FP&A, budgeting and forecasting, performance management, and strategic advisory. It equips professionals with the advanced management accounting skills needed to drive business performance, optimize financial strategies, and navigate complex financial transactions.
The high demand for CMAs across various industries and their significant salary advantage underscores the value and importance of this certification in the accounting and finance landscape.
Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE)
The Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE) certification is a highly respected credential that plays a crucial role in detecting and preventing financial crimes. It equips professionals with specialized knowledge and skills in forensic accounting, investigative techniques, and fraud detection methods, making them essential for safeguarding organizations against financial fraud schemes.
Role of CFE Certification in Detecting and Preventing Financial Crimes
- Forensic Accounting Expertise: CFEs possess advanced skills in forensic accounting, allowing them to thoroughly examine financial records and identify discrepancies that may indicate fraudulent activity. This expertise is critical for uncovering complex financial schemes and ensuring the integrity of financial statements.
- Investigative Techniques: CFEs are trained in various investigative techniques, including interviewing suspects, gathering evidence, and conducting thorough investigations. These skills enable them to efficiently and effectively investigate potential fraud cases and build strong cases for prosecution or remediation.
- Fraud Detection Methods: The certification equips professionals with a deep understanding of fraud detection methods, such as data analysis, trend analysis, and the use of sophisticated software tools to identify unusual patterns and red flags that suggest fraudulent behavior.
Specialized Knowledge and Skills Required for a CFE Certification
- Fraud Prevention and Deterrence: CFEs learn how to implement and manage anti-fraud measures within organizations, helping to create environments that discourage fraudulent activities. This includes understanding the psychological aspects of fraud and creating effective prevention strategies.
- Financial Transactions and Fraud Schemes: CFEs gain comprehensive knowledge of various financial transactions and the fraud schemes associated with them. This includes understanding how different types of fraud are perpetrated and how to identify signs of these schemes.
- Legal Elements of Fraud: The certification covers the legal aspects of fraud, including laws related to fraud, the rights of the accused, and legal procedures for prosecuting fraud cases. This legal knowledge is vital for ensuring that investigations and actions are compliant with the law.
- Investigation Processes: CFEs are trained in the systematic processes of conducting fraud investigations, from initial detection through to reporting findings. This includes the use of technology and data analytics in investigations and the management of investigative teams.
Organizational Benefits Provided by CFEs
- Early Detection and Reduced Losses: Organizations with CFEs on staff uncover fraud 40% sooner and experience fraud losses that are 54% smaller than those without CFEs. This early detection is crucial in minimizing the financial damage and operational disruptions caused by fraud.
- Enhanced Financial Health and Longevity: The presence of CFEs in organizations not only helps in detecting and preventing fraud but also contributes to the overall financial health and longevity of the company. Their expertise helps create robust internal controls and fosters a culture of accountability and transparency.
High Demand and Tangible Impact
The demand for CFE-certified professionals is underscored by the fact that 90% of Fortune 500 companies employ at least one CFE. This high level of employment reflects the critical role CFEs play in maintaining the financial integrity and operational security of large organizations.
CFEs bring tangible benefits to the organizations they serve, as evidenced by the statistics that show their ability to detect fraud more quickly and reduce associated losses significantly. Their skills in forensic accounting, investigative techniques, and fraud detection methods make them invaluable assets in the fight against financial crimes.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Career
Choosing the right accounting certification depends on your career goals and areas of interest. Whether it is the CPA, CMA, CIA, CFE, or a specialized certification, each offers unique benefits and opens up different career opportunities.
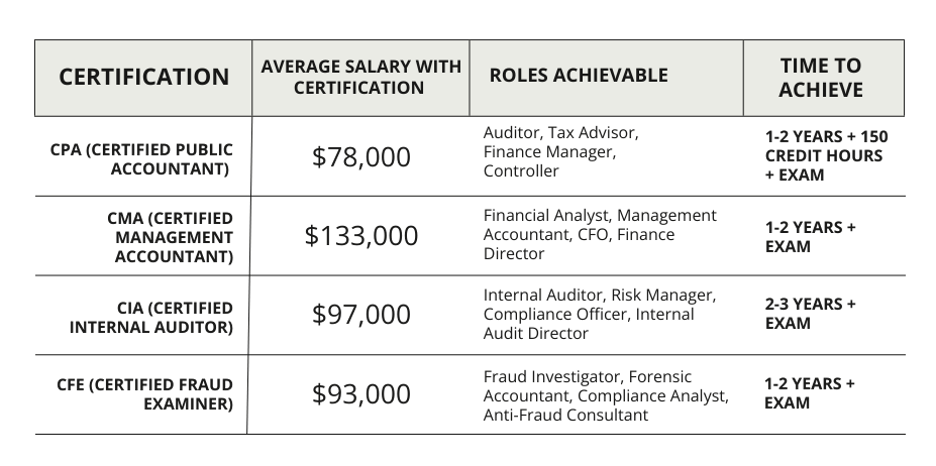
Remember, earning a certification is a significant investment of time and resources. It is essential to research each certification thoroughly and consider how it aligns with your long-term career aspirations. With the right certification, you can enhance your credibility, expand your career opportunities, and achieve your professional goals in the accounting field.









